Product Description
transmission parts rubber Motor Shaft Flexible Fluid Magnetic Spider Oldham coupler stainless steel Aluminum standard curved jaw Coupling
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Torque and Speed Limitations of Magnetic Couplings for Different Sizes and Applications
The torque and speed limitations of magnetic couplings depend on various factors, including the size of the coupling and the specific application requirements. Here’s a general overview of these limitations:
- Torque Limitations:
The torque capacity of a magnetic coupling is influenced by the strength of the magnets used, the size of the coupling, and the materials chosen for the rotor and containment shell. Larger magnetic couplings with stronger magnets and robust materials can handle higher torque requirements.
- Size and Application:
The size of the magnetic coupling plays a crucial role in determining its torque capacity. Smaller couplings are typically used in low-torque applications, such as laboratory equipment or small pumps. In contrast, larger couplings can handle higher torque demands, making them suitable for industrial-scale pumps and agitators.
- Speed Limitations:
The maximum speed at which a magnetic coupling can operate depends on several factors, including the rotational speed of the driving and driven shafts and the design of the coupling. High-speed applications, such as centrifugal pumps, require magnetic couplings designed to minimize eddy current losses and ensure stable performance at elevated speeds.
- Specialized Applications:
Some magnetic couplings are specifically designed for high-speed or high-torque applications, such as in large industrial pumps or agitators. These specialized couplings are engineered with materials and construction techniques to optimize performance under demanding conditions.
- Customization Options:
Manufacturers of magnetic couplings may offer customization options to tailor the torque and speed ratings to the specific needs of the application. This can involve selecting different magnet configurations, materials, and overall design adjustments to achieve the desired performance characteristics.
It is essential to consult with the coupling manufacturer or a qualified engineer to determine the appropriate magnetic coupling size, torque, and speed ratings for a specific application. Factors such as the fluid properties, load requirements, and environmental conditions should be taken into account to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and reliability.
Are Magnetic Couplings Suitable for High-Torque or High-Speed Applications in Various Industries?
Yes, magnetic couplings are suitable for high-torque or high-speed applications in various industries, depending on the specific design and material selection. These couplings offer distinct advantages that make them a viable choice for demanding applications with elevated torque and speed requirements.
Here’s how magnetic couplings perform in high-torque and high-speed scenarios:
- High-Torque Applications:
Magnetic couplings can handle high-torque applications efficiently. Neodymium and samarium cobalt magnets, known for their strong magnetic properties, enable magnetic couplings to transmit substantial torque without the need for physical contact. The absence of frictional wear and the robustness of these magnet materials make magnetic couplings well-suited for applications that demand high torque, such as large pumps, agitators, mixers, and heavy-duty industrial machinery.
- High-Speed Applications:
Magnetic couplings can also be designed for high-speed applications. The absence of physical contact between the driving and driven components reduces the risk of mechanical wear and allows magnetic couplings to operate smoothly at high rotational speeds. The magnetic fields effectively transmit power without compromising efficiency or generating excessive heat. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and precision machinery benefit from magnetic couplings’ ability to maintain performance and reliability at high speeds.
- Advantages in Various Industries:
Magnetic couplings find applications across diverse industries due to their ability to handle high-torque and high-speed requirements. Some notable industries where magnetic couplings are utilized include:
- Chemical and Petrochemical: Magnetic couplings are employed in pumps and agitators, where they prevent fluid leakage and provide a hermetically sealed solution. They are ideal for handling aggressive chemicals and corrosive substances.
- Pharmaceutical: In pharmaceutical processes, magnetic couplings are used in mixers and reactors to prevent contamination and ensure sterile operation.
- Automotive: Magnetic couplings find use in cooling systems, turbochargers, and various engine components to enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance.
- Renewable Energy: In wind turbines, magnetic couplings are utilized to transfer power between the turbine rotor and the generator, offering a maintenance-free and reliable solution.
- Food and Beverage: Magnetic couplings are employed in pumps and mixers for hygienic applications, ensuring no product contamination and meeting food safety standards.
Overall, magnetic couplings demonstrate versatility and effectiveness in high-torque and high-speed applications across multiple industries. Their ability to provide reliable power transmission without mechanical wear and the advantages of hermetic sealing make them an attractive choice for critical systems requiring efficiency, safety, and reduced maintenance.

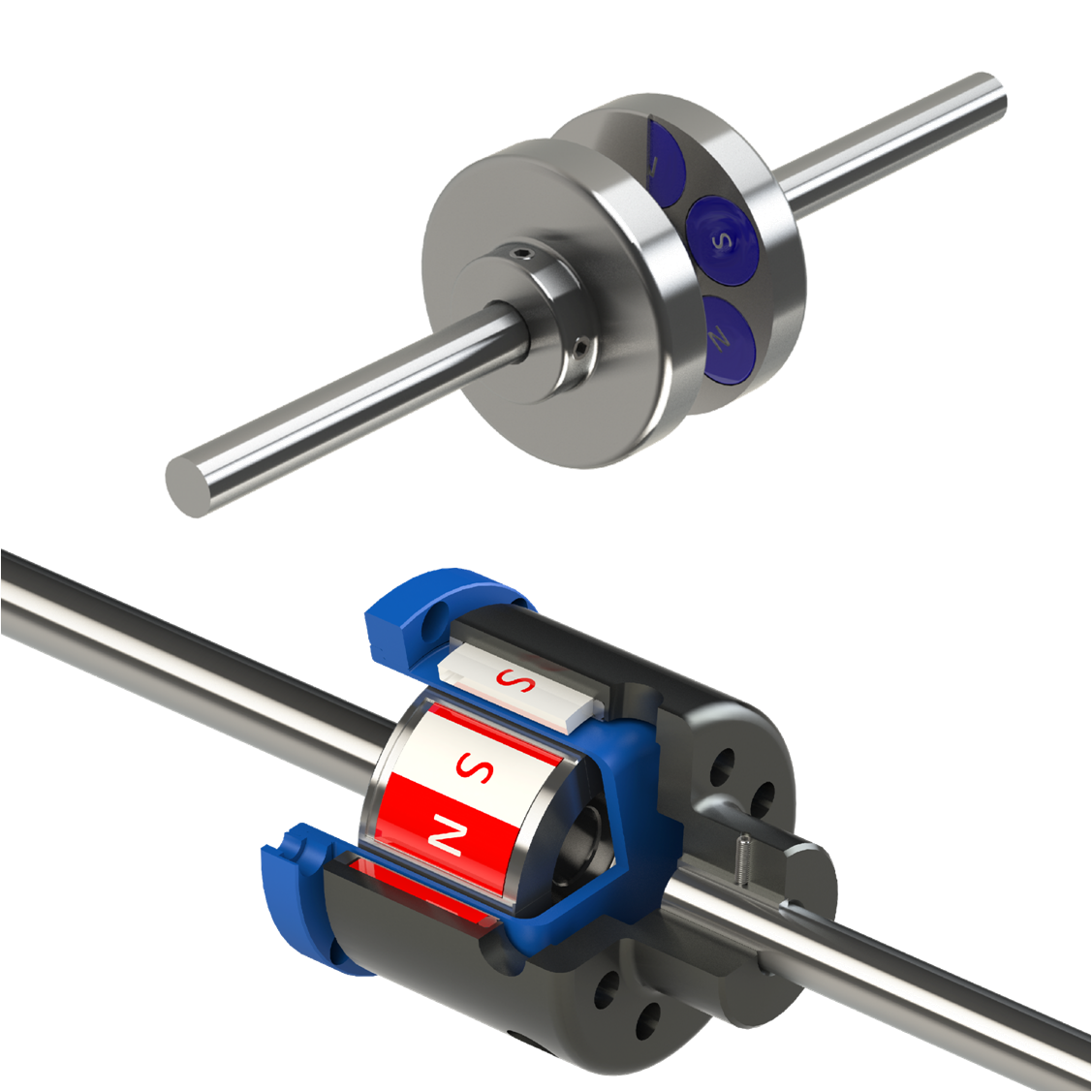
What is a Magnetic Coupling and How Does It Function in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A magnetic coupling is a type of coupling used in mechanical power transmission systems to transfer torque from one shaft to another without direct physical contact. It operates based on the principles of magnetism and is designed to transmit rotational power while allowing a degree of misalignment and isolation between the input and output shafts.
The basic components of a magnetic coupling typically include an outer and inner rotor, both containing permanent magnets. The outer rotor is connected to the input shaft, while the inner rotor is connected to the output shaft. These rotors are separated by a non-magnetic containment shell, creating a magnetic air gap between them.
When the input shaft rotates, the magnets on the outer rotor create a magnetic field that passes through the containment shell and induces a corresponding magnetic field in the inner rotor. The interaction between these magnetic fields causes the inner rotor to rotate synchronously with the outer rotor, effectively transferring torque from one shaft to the other.
The key features and functions of magnetic couplings in mechanical power transmission are as follows:
- Non-Contact Power Transmission:
Unlike traditional mechanical couplings that require physical contact between components, a magnetic coupling achieves torque transmission through magnetic fields, enabling a non-contact power transfer.
- Misalignment Compensation:
The magnetic coupling can accommodate a certain amount of misalignment between the input and output shafts. This feature helps prevent excessive forces and wear on the system, improving its overall reliability.
- Isolation and Containment:
The containment shell between the rotors isolates the input and output shafts, making the magnetic coupling ideal for applications where fluid or gas containment is critical. It allows for hermetically sealed connections in pumps, mixers, and other equipment.
- Overload Protection:
In case of sudden overload or jamming in the driven system, the magnetic coupling can slip or disengage, protecting the driving motor and components from damage.
- No Lubrication Requirements:
Since there is no physical contact, magnetic couplings do not require lubrication, reducing maintenance needs and the risk of contamination in sensitive applications.
- No Wear or Friction:
The absence of mechanical contact eliminates wear and friction between the coupling’s components, leading to a longer service life and higher efficiency.
Magnetic couplings find applications in various industries, such as chemical processing, food and beverage, medical devices, and pumps, where leakage prevention, cleanliness, and reliability are essential.


editor by CX 2024-03-07