Product Description
Propeller Shaft Coupling Vibrator for Magnetic Bracelet Water Couplings Flexible Chain Fluid Flange Stainless Steel Spacer
Application of Propeller Shaft Coupling
A propeller shaft coupling is a mechanical device that connects 2 shafts together. It is used to transmit torque and rotation between the shafts. Propeller shaft couplings are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Marine. Propeller shaft couplings are used in marine applications to connect the engine to the propeller.
- Industrial. Propeller shaft couplings are used in industrial applications to connect different pieces of equipment together.
- Agricultural. Propeller shaft couplings are used in agricultural applications to connect the engine to the driveline.
- Off-highway. Propeller shaft couplings are used in off-highway applications to connect the engine to the driveline.
- Other. Propeller shaft couplings are used in a variety of other applications, such as wind turbines and conveyor belts.
There are a variety of different types of propeller shaft couplings, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The type of coupling that is best for a particular application will depend on the specific requirements of that application.
Here are some of the advantages of using propeller shaft couplings:
- They can transmit high torque and rotation.
- They are durable and can withstand a variety of harsh conditions.
- They are easy to install and maintain.
- They are available in a variety of sizes and styles to fit different applications.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using propeller shaft couplings:
- They can be expensive.
- They can be difficult to align properly.
- They can wear out over time.
Overall, propeller shaft couplings are a versatile and reliable way to connect 2 shafts together. They are used in a variety of applications and can be a valuable asset in any fleet.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
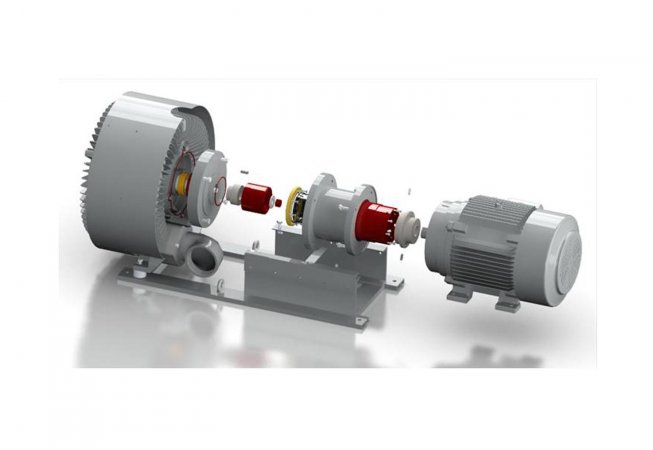

Can Magnetic Couplings Be Used in Applications Involving Corrosive or Aggressive Fluids?
Yes, magnetic couplings can be used in applications involving corrosive or aggressive fluids, provided that the coupling is constructed using materials that are compatible with the specific fluid being handled. The ability to use magnetic couplings with corrosive or aggressive fluids depends on the material selection and design of the coupling.
When handling corrosive or aggressive fluids, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Material Compatibility:
Select materials for the magnetic coupling that are resistant to the corrosive properties of the fluid. For example, stainless steel, Hastelloy, or certain grades of ceramics are commonly used for components that come into contact with corrosive fluids.
- Hermetic Sealing:
Ensure that the magnetic coupling provides a hermetic seal to prevent fluid leakage. The containment shell and other sealing components must be able to withstand the chemical properties of the aggressive fluid.
- Coatings and Lining:
In some cases, coatings or lining materials can be applied to the coupling’s surfaces that are exposed to the fluid. These coatings can offer additional protection against corrosion and ensure compatibility with aggressive fluids.
- Fluid Temperature and Pressure:
Consider the temperature and pressure of the aggressive fluid, as it may influence the material selection and design of the magnetic coupling. High temperatures or pressures can impact the coupling’s performance and material integrity.
- Fluid Properties:
Understand the specific chemical properties of the aggressive fluid, such as acidity, alkalinity, or reactivity. This information is crucial for selecting appropriate materials and ensuring the coupling can handle the fluid’s properties.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations:
Consult the magnetic coupling manufacturer for their recommendations on material selection and design considerations for applications involving corrosive or aggressive fluids. They can provide guidance based on their expertise and product specifications.
By carefully considering material compatibility and design factors, magnetic couplings can be successfully used in a wide range of applications involving corrosive or aggressive fluids. These couplings offer advantages such as leak-free operation, reduced maintenance, and the absence of wear-prone components, making them suitable for various industries, including chemical processing, petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals.

What materials, such as neodymium or samarium cobalt, are commonly used in manufacturing magnetic couplings?
Magnetic couplings utilize magnets made from various materials to transfer torque and power without physical contact. Some of the common materials used in manufacturing magnetic couplings include:
- Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB):
Neodymium magnets are the most widely used type of permanent magnets in magnetic couplings. They offer excellent magnetic properties, high energy density, and strong magnetic fields, making them highly efficient for power transmission. NdFeB magnets are known for their strong magnetic pull and are suitable for various applications with demanding torque requirements.
- Samarium Cobalt (SmCo):
Samarium cobalt magnets are another popular choice for magnetic couplings. They exhibit high magnetic stability, even at high temperatures, and have excellent corrosion resistance. SmCo magnets are often used in applications where extreme operating conditions, such as elevated temperatures or aggressive environments, are present.
- Alnico:
Alnico magnets are an older type of permanent magnet, known for their high magnetic strength and thermal stability. While not as powerful as neodymium magnets, alnico magnets are still used in certain magnetic coupling applications, especially in situations where the operating temperature is a critical factor.
- Ceramic Magnets (Ferrite):
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, are cost-effective and widely used in various magnetic coupling designs. They have moderate magnetic strength and are suitable for applications with less demanding torque requirements.
The selection of magnet material for a magnetic coupling depends on the specific application requirements, such as the desired torque transmission, operating temperature, and environmental factors. Manufacturers may also incorporate different magnet configurations and arrangements to optimize the coupling’s performance for a particular application.
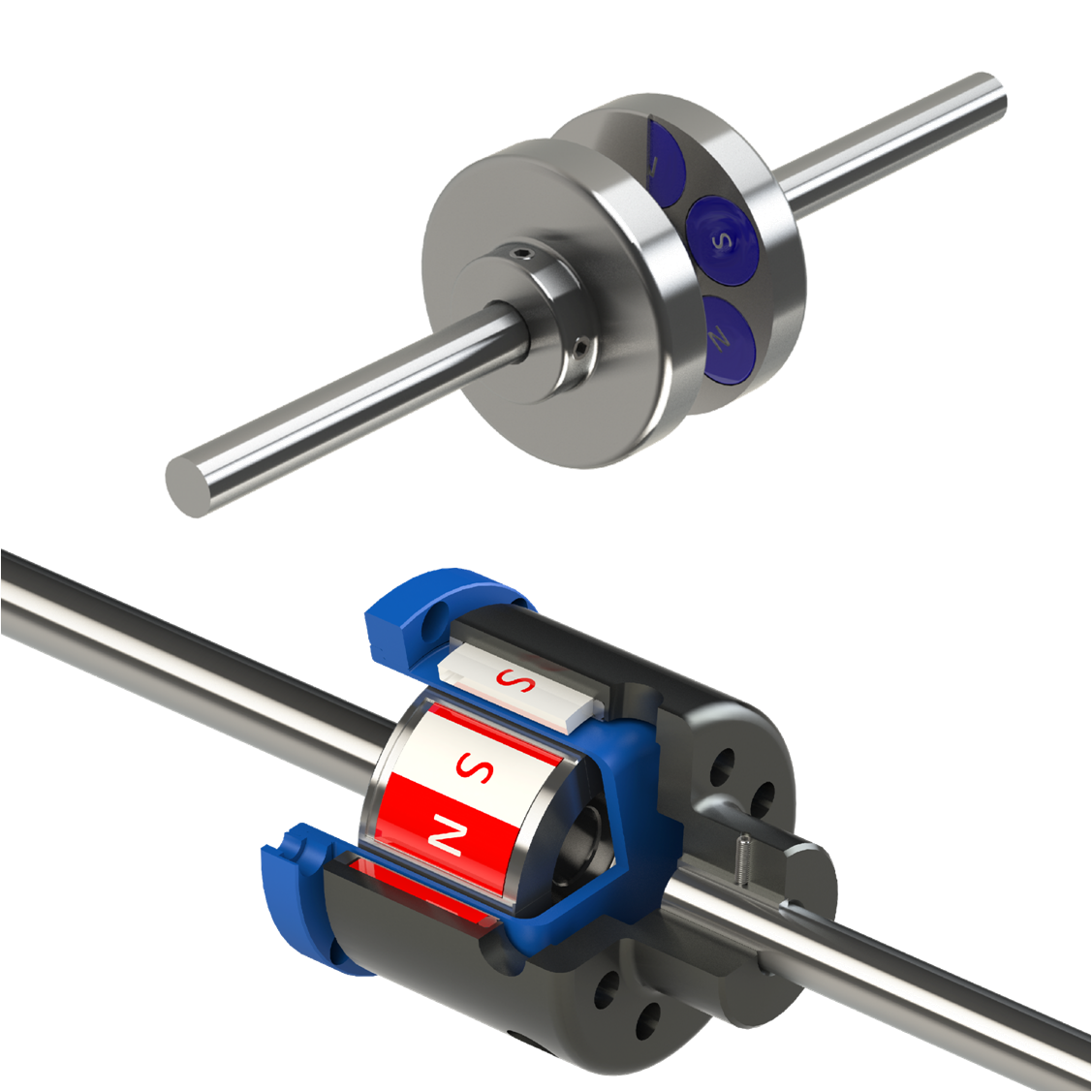
What is a Magnetic Coupling and How Does It Function in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A magnetic coupling is a type of coupling used in mechanical power transmission systems to transfer torque from one shaft to another without direct physical contact. It operates based on the principles of magnetism and is designed to transmit rotational power while allowing a degree of misalignment and isolation between the input and output shafts.
The basic components of a magnetic coupling typically include an outer and inner rotor, both containing permanent magnets. The outer rotor is connected to the input shaft, while the inner rotor is connected to the output shaft. These rotors are separated by a non-magnetic containment shell, creating a magnetic air gap between them.
When the input shaft rotates, the magnets on the outer rotor create a magnetic field that passes through the containment shell and induces a corresponding magnetic field in the inner rotor. The interaction between these magnetic fields causes the inner rotor to rotate synchronously with the outer rotor, effectively transferring torque from one shaft to the other.
The key features and functions of magnetic couplings in mechanical power transmission are as follows:
- Non-Contact Power Transmission:
Unlike traditional mechanical couplings that require physical contact between components, a magnetic coupling achieves torque transmission through magnetic fields, enabling a non-contact power transfer.
- Misalignment Compensation:
The magnetic coupling can accommodate a certain amount of misalignment between the input and output shafts. This feature helps prevent excessive forces and wear on the system, improving its overall reliability.
- Isolation and Containment:
The containment shell between the rotors isolates the input and output shafts, making the magnetic coupling ideal for applications where fluid or gas containment is critical. It allows for hermetically sealed connections in pumps, mixers, and other equipment.
- Overload Protection:
In case of sudden overload or jamming in the driven system, the magnetic coupling can slip or disengage, protecting the driving motor and components from damage.
- No Lubrication Requirements:
Since there is no physical contact, magnetic couplings do not require lubrication, reducing maintenance needs and the risk of contamination in sensitive applications.
- No Wear or Friction:
The absence of mechanical contact eliminates wear and friction between the coupling’s components, leading to a longer service life and higher efficiency.
Magnetic couplings find applications in various industries, such as chemical processing, food and beverage, medical devices, and pumps, where leakage prevention, cleanliness, and reliability are essential.


editor by CX 2023-12-19